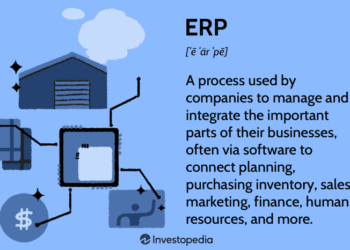
Exploring the realm of ERP implementation cost unveils a complex landscape of factors, components, budgeting strategies, and hidden expenses. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of determining and managing costs associated with implementing an ERP system, shedding light on crucial aspects often overlooked.
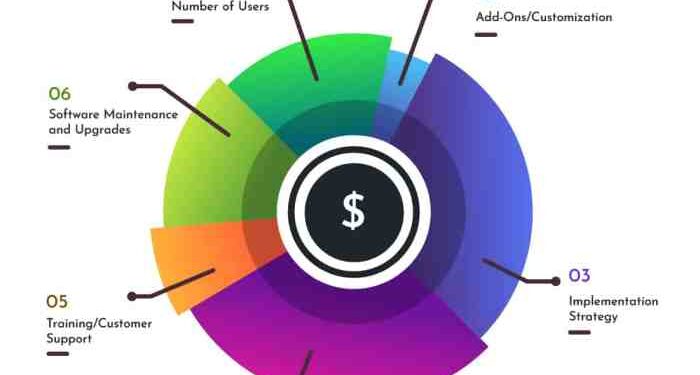
Factors impacting ERP implementation cost
ERP implementation costs can vary significantly based on several factors that influence the overall expenses. Understanding these factors and implementing strategies to mitigate their impact is crucial for a successful ERP implementation project.
Customization requirements
Customizing an ERP system to fit specific business needs can significantly impact implementation costs. The more customization required, the higher the cost. For example, if a company needs unique features or workflows that are not standard in the ERP software, developers will need to spend more time and resources to tailor the system accordingly.
To mitigate this cost factor, businesses can opt for ERP systems that offer a high degree of flexibility and configurability to reduce the need for extensive customization.
Data migration complexity
The complexity of migrating data from existing systems to the new ERP platform can also affect implementation costs. Data migration involves transferring large volumes of data, ensuring data accuracy, and mapping data fields between systems. The more complex the data migration process, the higher the costs.
To mitigate this factor, companies can invest in data cleansing and preparation before the migration to streamline the process and reduce errors.
Training and change management
Training employees on how to use the new ERP system and managing organizational change can add to implementation costs. Employee training is essential to ensure a smooth transition to the new system and maximize its benefits. Change management efforts, such as communication plans and stakeholder engagement, also contribute to overall costs.
To mitigate this factor, companies can develop comprehensive training programs and change management strategies to prepare employees for the ERP implementation.
Integration with third-party systems
Integrating the ERP system with existing third-party applications or systems can impact implementation costs. The complexity of integration, the number of systems involved, and the need for custom interfaces all contribute to the overall expenses. Companies can mitigate this cost factor by selecting an ERP system that offers robust integration capabilities and pre-built connectors for popular third-party applications.
Vendor selection and support
Choosing the right ERP vendor and securing adequate support for the implementation process is crucial for project success. The cost of vendor services, ongoing support, and maintenance can vary significantly and impact the total implementation cost. To mitigate this factor, businesses should conduct thorough research, request detailed proposals from vendors, and negotiate favorable terms for support and maintenance services.
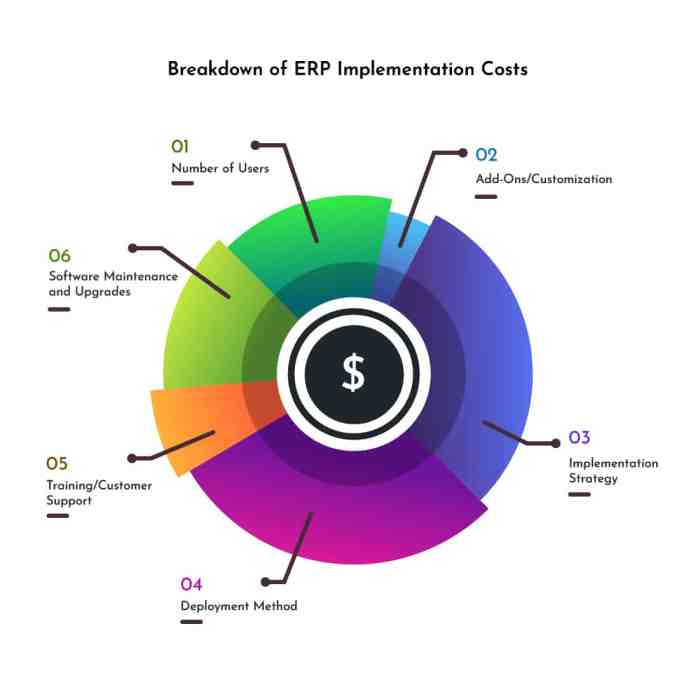
Components of ERP Implementation Cost

When considering the total cost of ERP implementation, it is essential to break down the various components that contribute to the overall expenses. Each component plays a significant role in the cost calculation and understanding their implications can help in managing the budget effectively.
Licensing Costs
Licensing costs refer to the fees associated with purchasing the ERP software license. These costs can vary depending on the number of users, modules required, and any customization needed. Licensing costs are often a significant portion of the total implementation cost and should be carefully considered.
Implementation Services
Implementation services include the costs of hiring consultants or experts to assist with the deployment of the ERP system. These services may involve customization, data migration, training, and ongoing support. The quality of implementation services can impact the success of the ERP project and should be budgeted accordingly.
Hardware and Infrastructure
Hardware and infrastructure costs cover the expenses related to servers, networking equipment, and other IT infrastructure needed to support the ERP system. These costs can vary based on the scalability and complexity of the ERP solution being implemented. It is essential to ensure that the hardware can handle the requirements of the ERP system without causing performance issues.
Training and Change Management
Training and change management costs involve educating employees on how to use the new ERP system effectively and managing the organizational changes that come with its implementation. Investing in comprehensive training and change management can help maximize the benefits of the ERP system and minimize resistance from employees.
Maintenance and Support
Maintenance and support costs include ongoing expenses for software updates, troubleshooting, and technical support. These costs are crucial for ensuring the long-term success and efficiency of the ERP system. It is important to factor in these costs when planning the overall budget for ERP implementation.
Budgeting for ERP implementation
Creating a budget for ERP implementation is a crucial step in ensuring the success of the project. It involves estimating and allocating costs effectively to manage resources efficiently.
Steps in Creating a Budget for ERP Implementation
- Identify the scope of the ERP project, including the modules to be implemented and the timeline for completion.
- Estimate the costs associated with software licensing, hardware procurement, implementation services, training, and ongoing support.
- Allocate resources based on the priority of different project components and the availability of funds.
- Create a detailed budget document outlining all projected expenses and contingency plans for unforeseen costs.
Best Practices for Estimating and Allocating Costs in ERP Implementation
- Engage with vendors and consultants to gather accurate pricing information for software, services, and training.
- Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, upgrades, and future scalability, when estimating costs.
- Review historical data from similar ERP projects to identify potential cost drivers and areas for cost savings.
- Regularly update the budget based on project milestones and changes in requirements to ensure accuracy.
Tips for Managing the Budget Throughout the Implementation Process
- Establish a dedicated budget management team to oversee expenses, track variances, and adjust allocations as needed.
- Implement cost control measures, such as monitoring spending against budgeted amounts and identifying cost-saving opportunities.
- Communicate budget updates and financial status to project stakeholders regularly to maintain transparency and accountability.
- Document all budget-related decisions and revisions to provide a clear audit trail for future reference.
Hidden costs in ERP implementation
During ERP implementation, organizations may overlook certain hidden costs that can have a significant impact on the overall budget and timeline of the project. These hidden costs can often arise unexpectedly, leading to budget overruns and delays if not addressed proactively.
Vendor lock-in costs
One common hidden cost in ERP implementation is vendor lock-in costs. These costs may occur when organizations become dependent on a specific vendor for ongoing support, upgrades, or customizations. Switching vendors later on can result in additional expenses and disruptions to the project timeline.
Data migration and integration costs
Another hidden cost to consider is data migration and integration costs. Moving data from legacy systems to the new ERP system and ensuring seamless integration with other applications can be more complex and time-consuming than anticipated. This can lead to additional costs for data cleansing, mapping, and testing.
Training and change management expenses
Training and change management expenses are often underestimated during ERP implementation. Providing comprehensive training for employees on the new system and managing resistance to change can require additional resources and investment. Neglecting these costs can result in lower user adoption rates and productivity.
Customization and maintenance costs
Customization and maintenance costs are frequently overlooked during ERP implementation. Tailoring the system to meet specific business requirements and ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal performance can incur additional expenses. Failure to account for these costs upfront can lead to budget overruns in the long run.
Ways to uncover and address hidden costs proactively
- Conduct a thorough analysis of potential hidden costs during the planning phase of the ERP implementation.
- Engage with stakeholders and vendors to identify any potential hidden costs early on and incorporate them into the budget.
- Allocate a contingency fund to account for unforeseen expenses that may arise during the implementation process.
- Regularly review and update the budget to ensure that any hidden costs are promptly addressed to avoid budget overruns.
Final Review
In conclusion, grasping the nuances of ERP implementation cost is essential for organizations embarking on this transformative journey. By understanding the factors at play, dissecting the components, mastering budgeting techniques, and unveiling hidden costs, businesses can navigate the financial aspects of ERP implementation with confidence and foresight.
User Queries
What are the key factors influencing ERP implementation cost?
The key factors include customization requirements, data migration complexity, scope of implementation, and vendor licensing fees.
How can organizations mitigate the impact of cost-influencing factors?
Organizations can mitigate costs by conducting thorough planning, prioritizing essential features, negotiating vendor contracts, and investing in employee training.
What are the main components contributing to ERP implementation cost?
The main components include software licensing, hardware infrastructure, implementation services, training, and ongoing support and maintenance.
How can companies effectively manage the budget during ERP implementation?
Companies can manage the budget effectively by tracking expenses, revisiting the budget regularly, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and communicating transparently with stakeholders.
What are some common hidden costs in ERP implementation?
Common hidden costs include additional customization needs, unforeseen data integration challenges, post-implementation support expenses, and system scalability requirements.